What are Structural Defects and why you should be concerned?
Structural defects in buildings refer to issues that affect the integrity, stability, or load-bearing capacity of the structure. These defects can arise from various factors, including design flaws, construction errors, material deterioration, or external forces such as seismic activity or environmental conditions. Here are some common types of structural defects:
-
Foundation Issues: Problems with the building’s foundation can lead to significant structural instability. Common foundation defects include settlement, differential movement (where different parts of the foundation settle at different rates), or inadequate support for the load imposed by the building.
-
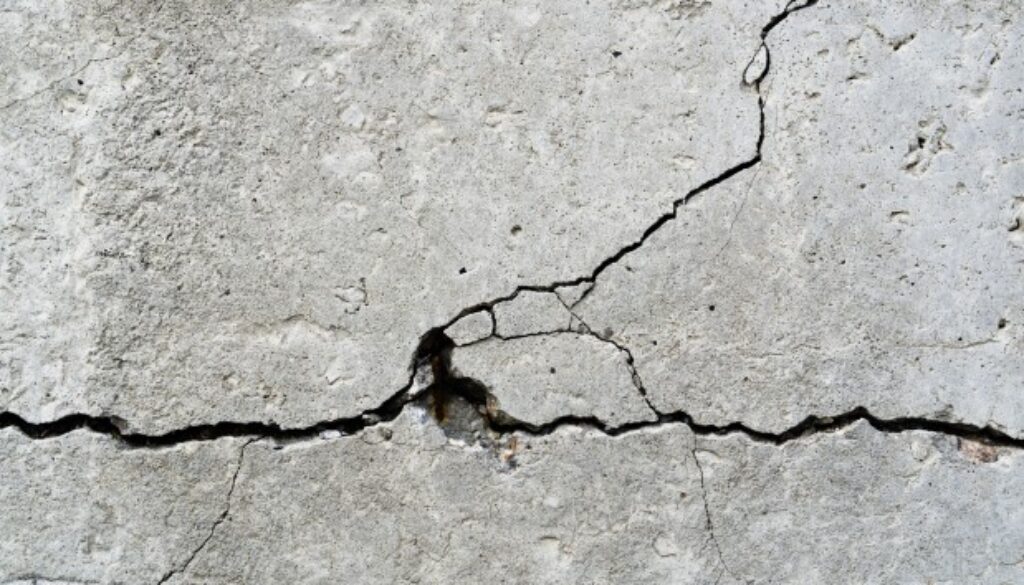
Cracks and Settlement: Cracks in walls, floors, or ceilings can indicate underlying structural issues. They can be caused by various factors, including poor construction practices, excessive loads, soil movement, or foundation problems. Different types of cracks can provide clues about the nature and severity of the structural defect.
-
Deficient Structural Members: Structural elements such as beams, columns, walls, or floors may exhibit defects due to poor material quality, inadequate design, or incorrect installation. These defects can compromise the overall strength and stability of the building.
-
Roof and Truss Problems: Issues with the roof structure, including sagging, rot, or inadequate support from trusses or framing members, can lead to structural instability and potential safety hazards.
-
Lateral Stability: Buildings need to resist lateral forces, such as wind or seismic loads, to maintain stability. Inadequate lateral stability systems, such as insufficient bracing or shear walls, can compromise the structural integrity of the building.
-
Overloading and Load Path Issues: Structural defects can occur if the building is subjected to loads beyond its intended capacity or if the load path is not properly distributed. This can result in excessive stress on certain elements, leading to failure or deformation.
When addressing structural defects, remedial building works may involve a range of solutions depending on the specific issue. These can include structural repairs, reinforcement or strengthening of existing members, underpinning or foundation stabilization, and, in extreme cases, partial or complete replacement of the affected components.
It’s important to note that identifying and addressing structural defects requires the expertise of structural engineers or qualified professionals experienced in building diagnostics and remedial works.
EAAE will conduct detailed inspections, assessments, and calculations to determine the extent of the defect and recommend appropriate remedial measures to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the building.